Sales journal
Content:
- Definition and explanation
- Sales invoice
- Format of sales journal
- Posting from sales journal to subsidiary and general ledger
- Example
- Sales journal with sales tax column
Definition and explanation
Sales journal (also known as sales book and sales day book) is a special journal used to record all credit sales. Every transaction that is entered in this journal essentially results in a debit to accounts receivable account and a credit to sales account. Cash sales are not recorded in sales journal rather they are recorded in another special journal known as cash receipts journal.
In context of this article, the term sales refers to the sale of only those goods or merchandise which the organization normally deals in. Any sale of used or outdated assets (like old plant, machinery, equipment and newspapers etc.) are not recorded in sales journal. These transactions are entered in general journal, also known as journal proper.
Sales invoice
When a seller sells merchandise on credit, he prepares an invoice known as sales invoice or outward invoice. This invoice is sent to the customer, usually along with the merchandise sold. Seller also prepares a duplicate copy of each invoice he sends out to his buyer. This duplicate copy is kept by the seller with him because the entry in sales journal is made on the basis of it.
Format of sales invoice
The specimen/format of a simple sales invoice or outward invoice with some basic information is given below:
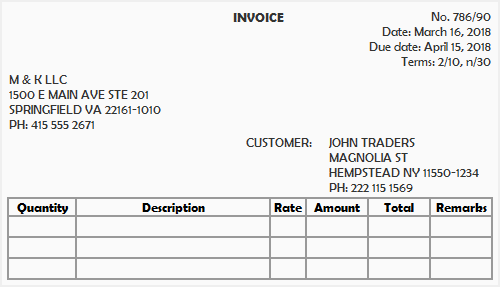
If you have already read “purchases journal” article, you may have noticed that the sales invoice and purchase invoice are two different names given to the same document. It is always prepared by the seller and is called sales invoice in the record of seller and purchase invoice in the record of buyer. The seller uses it to record a sales transaction in his sales journal and the buyer uses it to record a purchase transaction in his purchases journal.
Format of sales journal
The information recorded in a sales journal depends on the nature and needs of each individual business. However, a commonly used format of sales journal is given below:
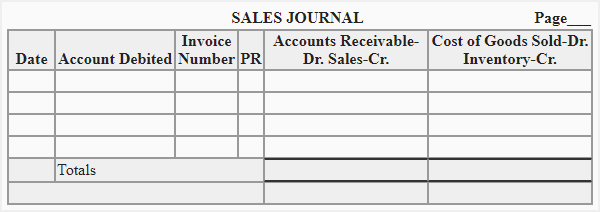
Explanation of columns
A brief explanation of columns used in above format of sales journal is as follows:
- Date: This column is used to record the date on which the sale is made. Normally, it is the same date as written on the sales invoice.
- Account debited: This column is used to enter the name of customers whose individual accounts are maintained in accounts receivable subsidiary ledger.
- Invoice number: The sales invoice number is written in this column.
- Post reference (PR): The entries in sales journal are posted to relevant accounts in receivables subsidiary ledger on daily basis. The post reference is used to enter the account numbers of individual accounts in subsidiary ledger to which the entries are posted.
- Accounts receivable & Sales: In this column, the net amount receivable from customers is written. In general ledger, the accounts receivable account is debited and sales account is credited by the total of this column.
- Cost of goods sold & inventory: In this column, the cost price of the merchandise sold is entered. In general ledger, the cost of goods sold account is debited and inventory account is credited by the total of this column.
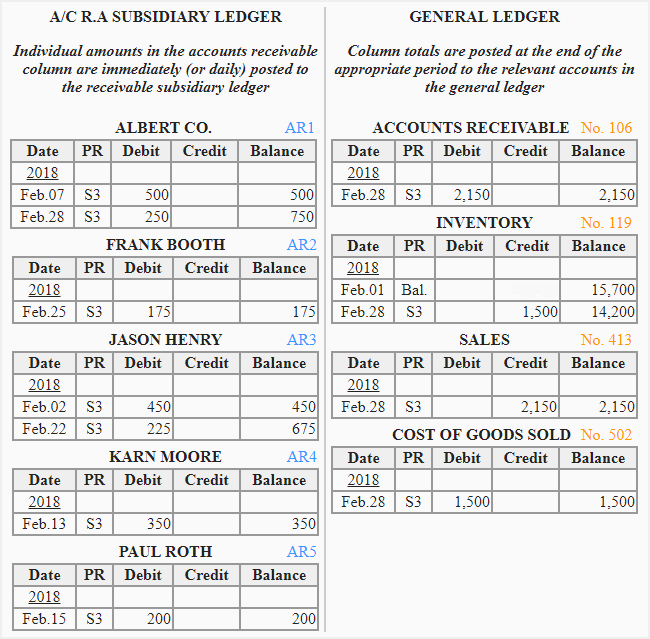
Posting entries from sales journal to subsidiary and general ledger
The entries in sales journal must be posted from sales journal to subsidiary and general ledger. This posting procedure is briefly explained below:
(1). Posting to accounts receivable subsidiary ledger:
At the end of each day (or immediately after the transaction has been performed), the individual entries are debited to appropriate accounts in accounts receivable subsidiary ledger.
(2). Posting to general ledger:
At the end of each month or another appropriate period, the column totals of sales journal are posted to relevant general ledger accounts as follows:
- The total of accounts receivable & sales column is debited to accounts receivable account and credited to sales account in the general ledger.
- The total of cost of goods sold & inventory column is debited to cost of goods sold account and credited to inventory account in the general ledger.
To indicate that the posting has been made to general ledger accounts, the account numbers of general ledger accounts are written in parentheses below the totals of the relevant columns of sales journal.
Consider the following example for a better explanation of the whole procedure.
Example
The following example illustrates how transactions are recorded in a sales journal and how entries from there are posted to subsidiary and general ledger.
Recording entries in sales journal
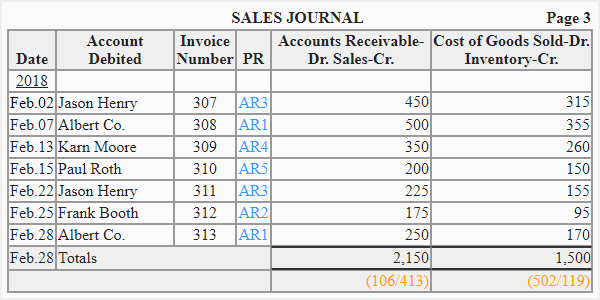
Posting entries from sales journal to ledger accounts
Sales journal with a “sales tax payable” column
The sellers are generally instructed by government to collect sales tax from their customers on the sale of certain goods and services and send the same to appropriate tax agency. If a business is collecting sales tax from customers, it is convenient to add a sales tax payable column to its sales journal. An example of sales journal with a sales tax payable column is given below:
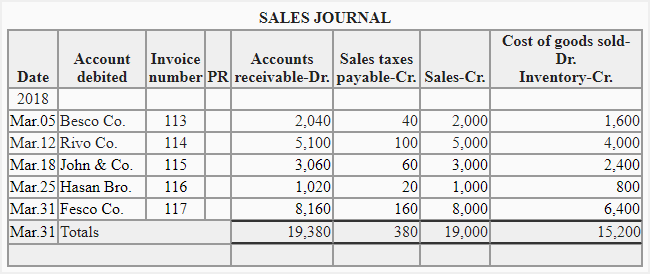
The sales journal given above shows that the seller is collecting sales tax @ 2% on all goods sold to customers. The posting of this sales journal will be similar to the posting explained in the above example.
A sales tax payable account is opened in general ledger and the total of sales taxes payable column is credited to that account at the end of each month or another appropriate period.

To know how to post transaction to sales journal
Cash payment journal