Account and its format
An account may be defined as a record to keep track of increases and decreases in financial statement items such as revenue, expenses, cash, machinery, accounts payable and loan etc. A separate account is maintained for each financial statement item. Normally, a firm or company maintains many accounts which are collectively known as ledger. The information about number and titles of accounts maintained by an entity is usually available in its chart of accounts.
Format of account
The simplest form of account has three parts:
- the account title or account name,
- a left side to record debit entries,
- a right side to record credit entries.
The format of account is given below:
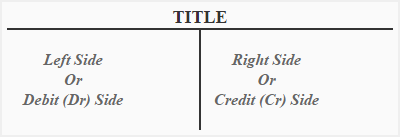
The account format shown above is known as T-account because it resembles the English letter “T”. The left side of the account is known as debit side and is abbreviated as Dr. The right side is known as credit side and is abbreviated as Cr. When an amount is written on the debit side, the account is said to be debited and when an amount is written on the credit side, the account is said to be credited. The debit and credit entries in an account are made according to certain rules of double entry accounting known as rules of debit and credit.
Example
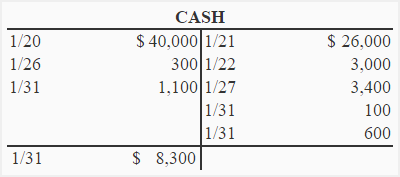
In cash account illustrated below, all cash receipts are entered on debit side and all cash disbursements are entered on credit side. See rules of debit and credit.
Balancing the account
The balance of an account is the difference between the total of debit entries and the total of credit entries in the account. If the total of debit entries exceeds the total of credit entries, the account has a debit balance; if the total of credit entries exceeds the total of debit entries, the account has a credit balance. In cash account illustrated above, the total of debit entries is $41,400 and the total of credit entries is $33,100. The total of debit entries exceeds the total of credit entries. The cash account therefore has a debit balance of $8,300 ($41,400 – $33,100). This balance has been written on the debit side below the line drawn following the last entry in the account. It represents the amount of cash that the business should have in hand at the date of balance i.e., January 31. If a balance sheet is prepared on January 31, the cash in the amount of $8,300 would be shown in the assets section.
Some more formats of account
(1). Account format with date, description and amount column on both sides.
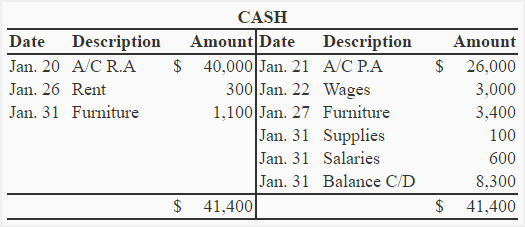
The format given above is a more professional form of T-account. In this format, the balance is put on the lighter side of the account. In our illustration, the credit side is lighter. The debit balance of $8,300 has therefore been put on the credit side of the account.
(2). Running balance account format:
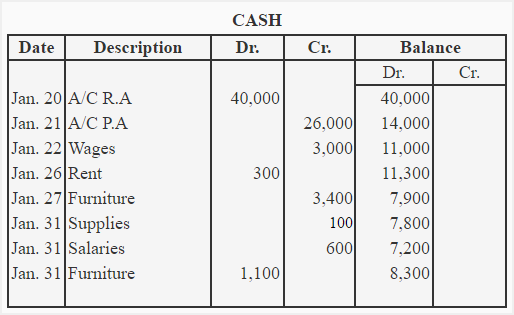
The T-account is used in situations where account balance is required periodically i.e., weekly, monthly, biannually or annually etc. Running balance account is helpful in situations where account balance is needed after each entry.
The account formats used in this article are easy to understand and are used in most of the educational materials for students. If you are using an accounting software, it might use a slightly different format. Regardless of the format used, the basic concept of recording entries in an account and finding its balance is the same.

Dear Sir, Accessed to study formats communicating the risks in the transactions for decision making
Thank you
Kalaranji Maheswaran
How do accountants write program memo and payment voucher?