Cumulative and noncumulative preferred stock
After common stock, preferred stock is the second popular class of equity instruments that corporations sell to manage funds for their operations. The preferred stock issued by a corporation generally belong to one of the two main types – cumulative or noncumulative.
This page briefly explains the meanings of and the difference between cumulative and noncumulative preferred stock.
Cumulative preferred stock
In case of cumulative preferred stock, any unpaid dividends on preferred stock are carried forward to the future years and must be paid before any dividend is paid to common stockholders. For example, a corporation issues 100,000 shares of $5 cumulative preferred stock on 1st January 2020 and does not pay any dividend during the first year of issue. The $5 dividend per share will be carried forward to the next year i.e., year 2021. If board of directors decides to pay a dividend of $1,200,000 in 2021, the cumulative preferred stockholders will be paid a total dividend of $1,000,000 ($5 per share for two years; $500,000 for 2020 + $5,00,000 for 2021). The remaining amount of $200,000 can then be distributed among common stockholders.
Disclosure of dividends in arrears on cumulative preferred stock
Any unpaid dividend on preferred stock for an year is known as ‘dividends in arrears’. The disclosure of dividends in arrears is an important financial indicator for investors and other users of financial statements. Such disclosure is made in the form of a balance sheet note. For example, the disclosure of the above dividend of $500,000 can be made on the balance sheet at the end of 2020 as follows:
Note 4: Dividends in arrears:
As of December 31, 2020, dividends on the $5 cumulative preferred stock were in arrears to the extent of $5 per share and amounted in total to $500,000.
Noncumulative preferred stock
Unlike cumulative preferred stock, unpaid dividends on noncumulative preferred stock are not carried forward to the subsequent years. If preferred stock is noncumulative and directors do not declare a dividend because of insufficient profit in a particular year, there is no question of dividends in arrears. For example, if a corporation issues 100,000 shares of $5 noncumulative preferred stock on 1st January 2020 and does not pay any dividend during the year 2020, the $5 dividend per share will not be carried forward to the year 2021. If board of directors decides to pay a dividend of $1,200,000 in 2021, the noncumulative preferred stockholders will be paid a total dividend of $500,000 ($5 per share for one year only – year 2021) and the remaining amount of $700,000 will then be distributed among common stockholders.
Example
The capital structure of Friends, Inc., is given below:
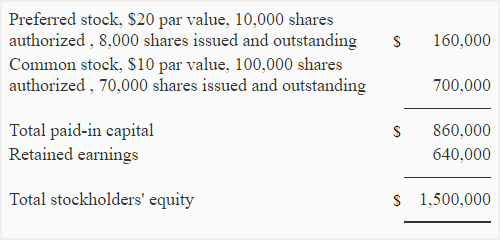
During the current year, management declared a dividend of $70,000. Dividend on preferred stock are 6% of par value which has been paid each year except for the immediate past year. The number of shares issued and outstanding of both the classes of stock have remained the same for last two years.
Required: Calculate the amount of dividend that will be paid to preferred stockholders and common stockholders if:
- the preferred stock is noncumulative.
- the preferred stock is cumulative.
Solution
Annual dividend on preferred stock:
160,000 × .06 = $9,600
(1). If the preferred stock is noncumulative:
Since the preferred stock is noncumulative in this case, the dividend on 6% outstanding preferred shares would be paid only for the current period. We would ignore any dividend in arrears in this case.

(2). If the preferred stock is cumulative:
Since the preferred stock in this case is cumulative, the dividend on 6% outstanding preferred shares would be paid for the current as well as for the past year i.e., the preferred stockholders will get a cumulative dividend of $19,200 (= $9,600 + $9,600) for two years.

In both the solutions above, notice that we have deducted the amount of dividend applicable to preferred shares from the total amount of divided announced during the year to obtain the amount of dividend applicable to common shares. It represents that the dividend on 6% preferred stock will be paid first to preferred stockholders and then the remaining amount can be deemed available for distribution to common stockholders. We have already talked about this point earlier in this article.
Further, the Friends Inc. needs to communicate the omitted dividends on preferred stock to the users of financial statements at the end of the past year by adding the following note to its year-end balance sheet:
Note xx: Dividends in arrears:
As of December 31, 20XX, dividends on 6% cumulative preferred stock were in arrears to the extent of $1.2 per share and amounted in total to $9,600.

Leave a comment